Fracture behaviour of elastomers under dynamic biaxial loading conditions
A biaxial testing machine from COESFELD enables essential new and more comprehensive opportunities for non-destructive and fracture mechanical testing of elastomers, mainly under dynamical load.

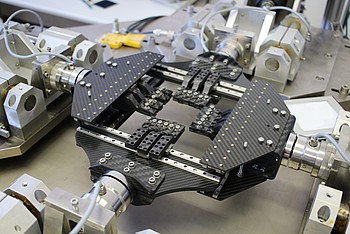
The Biax Tester consists mainly of 4 separately driven electro-mechanical linear motors, each with load cell and displacement sensor as well as a clamping system, which are arranged paired on opposite sites and have each a displacement range of 30 mm.
The motors are controlled separately; they can transfer different deformation (overall load configurations) to the sample. For the preferable dynamic tests each motor has an adaptive controller which realizes the desired deformation profile. Each clamping system consists of a rail with up to 10 individual clamps with a width of each 10 mm, which can slide by a wheel bearing transversal to the loading axis.
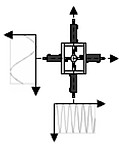
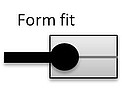
Sketch of the Test Stand with individually configurable displacement profiles for each axis (left); clamping system of the Biax Tester, here with 6 individual clamps per axis (middle), principle of clamping by form fit (right)
Specifications of the Biax Test Stand
| Excitation | Each axis separately or also pair-wise parallel feed |
| Displacement | Sine Wave, Gauss-Pulse, Triangle, Rectangle, freely defined by the user |
| Load speed | Max. 50 Hz, practically 10 Hz, max. displacement each up to 30 mm |
| Load range | 2000 N |
| Data acquisition | Whole cycles, individual cycles or individual parameters of the cycles |
| Image acquisition | Continuous or triggered by individual events |
| Sample size | Rectangular or squared with up to 100 mm * 100 mm, preferable 85 mm * 85 mm with circumferential cylindrical bulge with a diameter of 4 mm |
Mainly for the investigation of heterogeneous stress stages, like e.g. in samples with a crack, it is necessary to capture the 2d strain stage of the sample by image processing techniques. This is possible following the deformation of a random pattern at the sample surface and evaluation (Digital Image Correlation, DIC) or by recording the crack contour by homogeneous illumination of the sample from the bottom side (Digital Image Elaboration (DIE)). For these tasks an IR camera is used, which can be mounted feely on the ground plate by magnets.
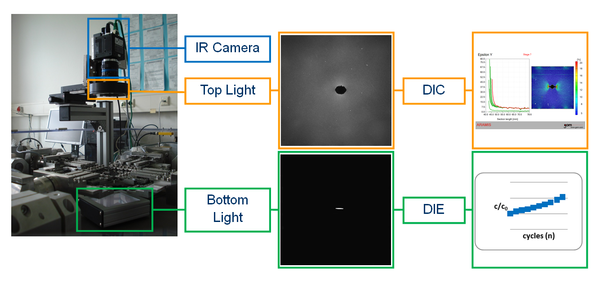
The camera can be adapted for the different tasks, especially recording the whole sample as well as of individual details of the sample each with optimal resolution.
The new Biax Test Stand of COESFELD strongly extends the static as well as dynamic characterization methods of elastomers. It delivers parameters for constitutive materials modelling under complex load, but also enables to trail the crack propagation under static as well as dynamic load, e.g. by the concept of J-integral.
G. Heinrich et al., Tire Technology 2014

